The introduction of 270-243.43 is bringing about an unparalleled transformation in the commercial environment, essentially altering the way organizations function and contend. This creative code represents a technological breakthrough that upends established norms and opens the door to ground-breaking inventions. Leaders in the industry and specialists have noticed that it has the capacity to revolutionize a number of fields and to propel substantial advancements.
Across a wide range of sectors, 270-243.43 has significantly increased productivity, efficiency, and overall performance since its launch. This essay will examine the history of this revolutionary technology, look at its present uses, and show how it is changing several industries. Along with discussing the tool’s possible future uses, we’ll also take a closer look at real-world case studies that show off its use.
Readers will have a thorough knowledge of why 270-243.43 is hailed as a real game-changer in the quickly changing corporate world by the end of this essay, emphasizing its significance in fostering innovation and improving operational skills.
Understanding 270-243.43: A Game-Changer in the Industry

The Emergence of 270-243.43 is significantly influencing the industry, reshaping traditional practices and creating exciting new pathways for innovation. To appreciate its impact fully, it’s crucial to explore its definition, historical background, essential components, and technical specifications.
Defining 270-243.43 and Its Historical Context
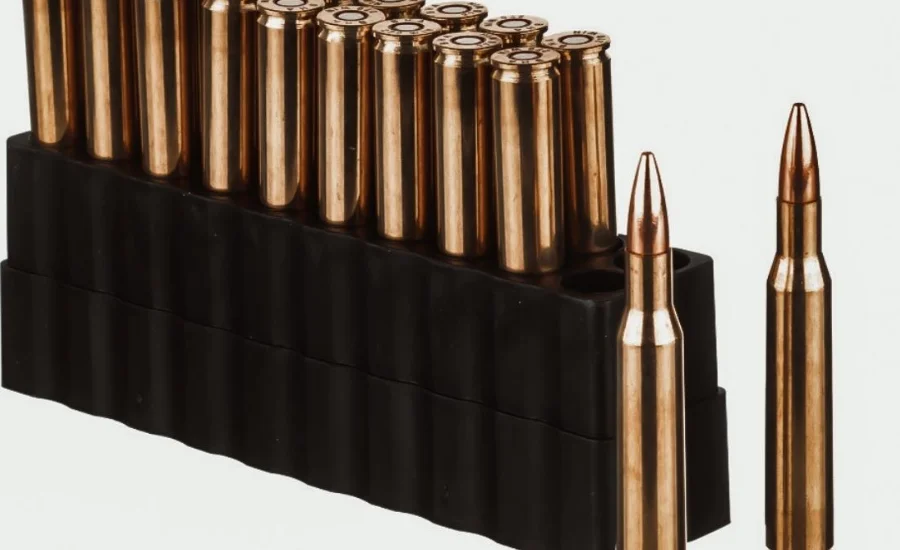
Fundamentally, 270-243.43 represents an incredible technological advancement that combines characteristics from two popular cartridges: the 243 Winchester and the 270 Winchester. These cartridges have a long history; the 270 Winchester and 243 Winchester were introduced in the first half of the 20th century, respectively. Both were painstakingly created to meet specific needs in the shooting and hunting communities. The 243 Winchester is valued for its perfect balance of power and controllable recoil, while the 270 Winchester is praised for its fast velocity and level trajectory.
This technological synthesis not only illustrates the history of firearms but also shows how technological improvements can result in the creation of adaptable instruments that meet a variety of user needs. The 270-243.43 is proof of the ongoing innovation in this industry, opening doors for new uses and improving the experience for both experts and hobbyists.
Essential Components of 270-243.43: A Technical Overview
The 270-243.43 represents a sophisticated integration of advanced features that contribute to its performance and versatility in various applications. Understanding its key components is essential to appreciate how this innovative system operates effectively.
Cartridge Case
At the heart of the 270-243.43 is its cartridge case, which is built upon the robust design of the 308 Winchester. This design lineage traces back to the 30-06 Springfield, lending strength and reliability to the cartridge system. This solid foundation is crucial for ensuring consistent performance under diverse shooting conditions.
Bullet Specifications
The 270-243.43 system accommodates bullets of varying calibers, specifically .277 caliber for the 270 component and .243 caliber for the 243 component. This diversity allows for a broad range of applications, making the system suitable for both hunting and target shooting. The ability to switch between these calibers enhances its adaptability, catering to different user preferences and requirements.
Propellant Characteristics
To achieve optimal velocity while maintaining safety, the propellant used in the 270-243.43 is meticulously engineered. This propellant formulation is designed to deliver high performance without compromising pressure levels, ensuring a balance between power and safety during operation.
Reliable Ignition
A critical element of the system is the high-quality primer, which guarantees reliable ignition across various environmental conditions. This component plays a vital role in the overall effectiveness of the cartridge, ensuring consistent firing regardless of external factors.
Together, these components form the backbone of the 270-243.43 system, contributing to its reputation as a versatile and dependable option in the field of shooting sports.
Technical Specifications of 270-243.43: A Comprehensive Insight
The innovative design of 270-243.43 is reflected in its detailed technical specifications, which highlight its versatility and performance capabilities.
Cartridge Dimensions
The 270-243.43 system features distinct cartridge dimensions for each of its components. The 243 Winchester cartridge has an overall length of 2.71 inches and a case length of 2.045 inches, while the 270 Winchester cartridge measures 3.34 inches in overall length with a case length of 2.54 inches. These dimensions play a crucial role in the system’s adaptability and efficiency.
Bullet Weights
The 243 Winchester can have bullet weights ranging from 55 to 115 grains; the most popular weights are 55, 87, 90, and 100 grains. By comparison, the 270 Winchester has bullet weights ranging from 130 to 160 grains, the most common being between 130 and 150 grains. This variation enables shooters to choose the best bullet for their particular application, be it target practice or hunting.
Velocity Performance
Velocity is a critical aspect of ammunition performance. The 243 Winchester achieves muzzle velocities between 2,960 and 3,020 feet per second, depending on the bullet weight. Meanwhile, the 270 Winchester delivers impressive muzzle velocities of around 3,140 feet per second when using 130-grain bullets. This difference in velocity contributes to the effectiveness of each cartridge in various shooting scenarios.
Energy Output
The 270 Winchester component is notable for providing 22% to 44% more muzzle energy compared to loads from the 243 Winchester. This increased energy translates to better performance, making the 270-243.43 system particularly effective for a range of applications, including larger game hunting.
Ballistic Coefficients
Ballistic performance is further defined by the coefficients of the cartridges. The 243 Winchester features ballistic coefficients ranging from 0.365 to 0.409, varying with the bullet design. In comparison, the 270 Winchester offers a broader range of ballistic coefficients from 0.372 to 0.536, enhancing its trajectory and accuracy.
Action Type
Regarding action types, the 243 Winchester is categorized as a short action, while the 270 Winchester falls under standard or long action classifications. This distinction influences the firearm’s configuration and handling characteristics, contributing to the user experience.
The 270-243.43 system effectively combines these specifications to deliver a powerful and adaptable solution tailored to meet the diverse demands of the industry. By merging the strengths of both the 270 Winchester and 243 Winchester cartridges, it addresses individual limitations and stands out as a transformative innovation. This duality of design has positioned 270-243.43 as a groundbreaking technology with significant implications across various sectors, redefining performance standards in the field.
The Pre-270-243.43 Landscape: Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations

Before the advent of 270-243.43, various industries operated within a framework defined by traditional methods that presented numerous challenges and limitations. This exploration of the industry landscape highlights how these conventional approaches shaped the operational practices of several key sectors.
Traditional Methods and Their Challenges
Industries heavily relied on time-honored techniques that had persisted for decades.Even though some of these techniques had some degree of effectiveness, they were frequently labor-intensive and ineffective. For instance, although making great progress since its founding, the textile industry—one of the biggest and oldest in the world—has found it difficult to completely modernize its operations. Despite improvements, many textile companies found themselves hampered by outdated practices that limited their competitiveness and adaptability.
Similarly, the paper and pulp industry, which has a long-standing history, experienced gradual innovations over the years but continued to depend on traditional manufacturing techniques. Smaller companies entered the market, producing specialty papers tailored for niche applications such as printing, packaging, and hygiene products. Yet, the overarching reliance on conventional methods hindered broader industry evolution.
In the automotive sector, a critical driver of global economies, traditional manufacturing practices were deeply entrenched. The industry focused predominantly on internal combustion engines and conventional materials, with minimal attention given to fuel efficiency and environmental sustainability. This narrow approach limited the potential for innovation, leaving significant gaps in meeting the demands of a changing market.
The chemical industry, with its origins dating back to ancient civilizations, also experienced limited change. Although it evolved during the Industrial Revolution, many processes remained largely unchanged, relying on established methods for large-scale chemical production. This stagnation prevented the sector from embracing modern advancements that could enhance efficiency and sustainability.
In summary, the pre-270-243.43 landscape was characterized by industries bound to traditional methods that, while functional, were often inefficient and restrictive. The introduction of 270-243.43 represented a significant shift, paving the way for innovation and progress across these sectors by addressing the limitations inherent in conventional practices.
Overcoming the Limitations of Traditional Methods in Industry

Traditional methods utilized across various sectors have long posed significant limitations, stifling progress and efficiency. These challenges not only impacted operational effectiveness but also raised concerns about environmental sustainability.
Environmental Impact and Industry Challenges
One of the foremost issues was the detrimental environmental footprint associated with many industries. In the textile sector, excessive water consumption and pollution were critical concerns, leading to significant ecological degradation. Similarly, the paper and pulp industry confronted serious challenges related to deforestation and the chemical pollutants released during production, raising alarms among environmental advocates.
The automotive industry faced mounting pressure to comply with stringent emissions standards while striving to produce vehicles that were both fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly. This necessitated a comprehensive reevaluation and overhaul of established manufacturing processes, which was no small feat given the industry’s historical reliance on traditional approaches.
In the chemical sector, safety concerns were paramount, particularly regarding the management of hazardous materials. The industry’s practices also attracted scrutiny over their environmental impact, highlighting the urgent need for more sustainable methodologies.
The energy sector, responsible for the production and distribution of various energy forms, encountered obstacles linked to environmental degradation, political instability, and economic fluctuations. These challenges further complicated efforts to transition to cleaner energy sources.
The building and construction industry, despite its foundational role in society, grappled with significant environmental issues, including deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution from construction materials. These practices not only threatened ecosystems but also posed health risks to communities.
The agricultural sector, vital for global food supply, similarly raised red flags due to its environmental consequences. Concerns about water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions underscored the need for innovative practices to enhance sustainability.
Lastly, the mining industry, one of the oldest sectors, continued to be fraught with danger. Workers often found themselves in hazardous conditions, facing the risk of injuries despite technological advancements that promised more efficient and safer extraction methods.
In light of these extensive challenges, the need for innovation and new strategies became increasingly apparent. The introduction of 270-243.43 has revolutionized how industries address these pressing issues, providing solutions that promote efficiency, sustainability, and environmentally conscious practices. This transformation not only reshapes the industrial landscape but also paves the way for a more sustainable future.
Read More: 726-210-2473
Final Words
With the implementation of 270-243.43, long-standing issues and restrictions related to conventional techniques are addressed, signaling a momentous shift in a number of industries. This discovery has the potential to transform operating processes, improve efficiency, and advance sustainability across several industries by utilizing cutting-edge technologies.
270-243.43 provides an innovative solution that not only mitigates environmental issues, regulatory demands, and the need for modernization in industries, but also creates new opportunities for growth and innovation. Its capacity to raise output while lowering environmental impact highlights how revolutionary it is in the quickly changing corporate environment of today.
In conclusion, 270-243.43 represents not just a technological advancement, but a comprehensive approach to fostering a more sustainable and efficient industrial future. Its impact will undoubtedly resonate across sectors, driving a cultural shift towards responsible practices and paving the way for continued innovation in the years to come.
For More Information Check It Out Twinkle Crest