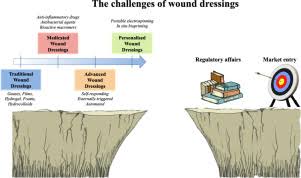
Wound care is one of the critical areas of health care that has evolved over time. The technologies in advanced wound care complement and, at times, supplant the traditional age-old wound care methods. Healthcare practitioners and patients should be aware of the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches to determine the appropriate treatment for their wound conditions
Traditional Wound Care Methods
Traditional wound care primarily uses primary dressings, topical antiseptics, and wound cleaning by hand. Some of them are-
Gauze Dressing: These are primarily used because of their availability and relatively low costs. They are simple to use and elementary. They take up the exudate and keep the wound out of the reach of the exterior contamination.
Antiseptics: Hydrogen peroxide, iodine, alcohol, and other liquids mainly treat infections and prevent outbreaks.
Manual Debridement removes dead tissue, dirt, or debris from the wound site for healing.
Pros of Traditional Wound Management
Cost-Effective: The traditional process is inexpensive as compared to the advanced procedures. Gauze and other easily accessible antiseptics are cheap and thus accessible in different care settings.
Accessibility: Traditional wound care products are relatively common in most clinics and pharmacies, making them available in most areas, including those underserved.
Cons of Traditional Wound Care
Limited Efficacy: First-line treatments may not be as effective in complex wounds, such as diabetes or pressure ulcers, where chances are there that advanced techniques might work.
Frequent Dressing Changes: Modern wound dressings usually require frequent changes. Removing the dressing is painful, and there is always the danger that every dressing change will be contaminated.
Pain and Trauma: Manual cleaning and Debridement can be painful for patients. It can cause a good amount of anxiety and even unease during recovery.
Advanced Techniques in Wound Care
Advanced wound care involves many modern treatments adapted to heal faster and more effectively. These include special dressings, growth factors, and even bioengineered tissues.
Hydrocolloid and Foam Dressings offer a moist healing environment and may manage exudate better than gauze.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): Negative pressure is applied to a wound inside a sealed dressing, which enhances blood flow and decreases edema to promote healing.
Bioengineered Skin Substitutes: Such devices can encourage the formation of a new tissue scaffold; the most helpful devices are those used for chronic or nonhealing wounds.
Pros of Advanced Wound Care
Healing Time: Advanced methods allow the healing process to take shorter periods with minimal chances for complications, especially in complex wounds.
Pain Management: Most advanced dressings reduce the trauma caused during dressing changes and provide better pain management for the patient.
Individualized Treatment: Advanced wound care methods can be adjusted according to the needs of the wound or patient, allowing for better results.
Cons of Advanced Wound Care
Cost-advanced wound care technologies are typically much more expensive than other traditional approaches, meaning there would be limited access for different patients and health care systems.
Training Needs- appropriate use and control of the management of advanced wound care techniques typically require specialized training; therefore, not all of them may be available in all areas.
Limited access to advanced wound care products and techniques may be experienced in some regions, especially the rural or underserved areas.
The choice of wound care should be specific to the patient, dependent on the type of wound and the facilities available in any given health facility; it will go along with the healing outcomes.