Key Takeaways:
- Vaping is often perceived as a safer alternative to smoking, but it comes with its own set of health risks.
- Research continues to investigate the potential link between vaping and cancer.
- Understanding the ingredients in vape liquids is crucial for assessing risk factors.
- There are supportive resources available for those seeking to quit vaping.
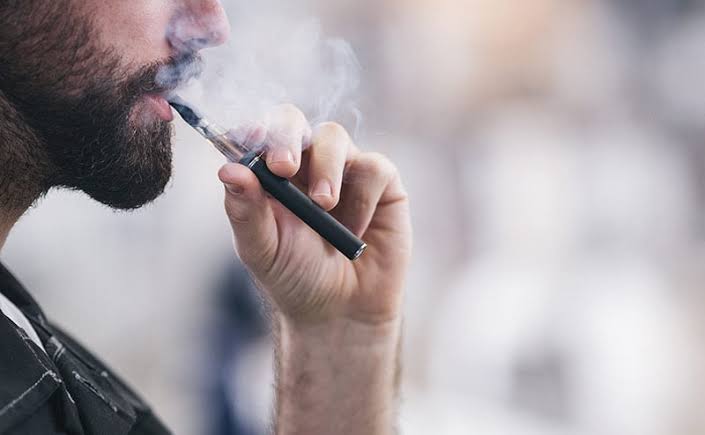
The Rise of Vaping: A Double-Edged Sword
The allure of vaping has become a global phenomenon, attracting millions, including teenagers, due to its image as a “healthier” alternative to smoking traditional cigarettes. As companies have aggressively marketed e-cigarettes, presenting them as a modern, less harmful alternative, the public perception has steadily shifted towards viewing these devices as a safer method to transition away from smoking. However, vaping is not without its complications. It represents a double-edged sword; on one side, it might help reduce exposure to certain hazardous chemicals in cigarette smoke. Still, on the other hand, the e-cigarette products introduce their own set of variables and potential health risks that are often underestimated or unknown. Questions like does vaping cause lung cancer continue to be pertinent and urge a deeper examination of vaping’s impact on health, making it essential for individuals to weigh the benefits against the risks cautiously.
Ingredients Matter: What Are You Inhaling?
Dissecting the composition of vape liquids is crucial for understanding the potential risks. These “e-juices” typically contain propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin as their base, serving as carriers for nicotine and flavorings. While both chemicals are considered safe by regulatory standards when used in food or cosmetic products, their safety profile when heated and inhaled as vapor remains under-explored over extended periods. At the heart of these liquids is nicotine, a powerful and addictive substance, which remains the primary reason for dependency. The many flavoring agents used to attract a broader audience, particularly youth, introduce further variables. Some research has suggested that when these flavorings undergo heating, they can produce harmful compounds such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde, which have recognized carcinogenic properties. This scenario complicates the narrative around nicotine and raises significant questions about the long-term health consequences for unsuspecting users who often assume they are inhaling a “safer” product.
The Potential Link to Cancer
While vaping is often embraced as the “safer” alternative for those seeking to quit smoking, emerging scientific scrutiny suggests a possible connection to cancer that merits careful consideration. Initial investigations have pointed out that even though e-cigarettes do not burn tobacco, the vapor they produce might still contain carcinogenic elements capable of causing cellular damage. According to the American Cancer Society, toxicants such as formaldehyde and acrolein have been identified in the vapors emitted by e-cigarettes. Although typically present at lower levels compared to traditional cigarette smoke, these substances are still capable of inducing cellular mutations, potentially leading to cancer over time. However, the science in this area is still evolving, requiring further extensive research and longitudinal studies to comprehend the breadth and depth of these potential risks fully. As scientists unravel these complexities, it becomes crucial for the public to stay informed and for public health messaging to adapt, ensuring that individuals can make informed choices about their use of vaping products.
Understanding Nicotine Dependency
Nicotine is the elastic thread that ties together the world of traditional smoking and vaping, and it is this compound that lies at the heart of addiction. It activates the brain’s reward pathways, reinforcing behavioral patterns that compel individuals to continue consumption. While many individuals approach vaping as a method to reduce their nicotine intake gradually, it often sustains or even escalates their dependency. This misconception that vaping is less addictive than smoking arises from the industry’s often inadequate regulation and labeling, which results in consumers potentially ingesting higher doses of nicotine than anticipated. Over time, this sustained consumption can solidify deeply entrenched habits, complicating attempts to cease nicotine use.
Health Implications Beyond Cancer
While the potential link between vaping and cancer is a predominant concern, it’s essential to acknowledge other health implications associated with vaping. For instance, recent studies have highlighted the potential impact on cardiovascular health. Some evidence suggests that the regular inhalation of vape aerosols can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, posing additional risks for cardiovascular complications. Moreover, research has shown that exposure to these aerosols can induce inflammation and oxidative stress, contributing factors to numerous chronic illnesses. Furthermore, the impact on respiratory health cannot be ignored. Emerging data indicates that vaping may lead to lung inflammation and reduced ability of the lungs to clear mucus, weakening the respiratory system’s defenses against infections. Recognizing these broader health effects is crucial for providing a comprehensive view of the risks associated with vaping and underscores the importance of ongoing research.
Creating Balanced Health Messaging
Effectively conveying the risks and realities of vaping requires a nuanced and balanced drawing board that emphasizes informed decision-making over sensationalism. As public health campaigns evolve to address this dynamic issue, they are tasked with providing comprehensive strategies that educate the public rather than inciting undue alarm. While it remains essential to delineate the potential risks associated with vaping, it is equally vital to recognize that not every user will experience significant adverse effects. Campaign efforts should approach vaping with measured responses, providing clear and actionable advice that equips individuals with the data necessary to make enlightened choices concerning their health. Supporting the public in pursuing healthier lifestyle choices involves respecting their autonomy and empowering them with knowledge, driving home the message that well-informed decisions are within reach and accessible to everyone.
Final Thoughts
The intricate and ever-evolving conversation around vaping navigates multiple layers of health implications, requiring steadfast commitments from researchers, health professionals, policymakers, and the public. As new data continues to emerge, illuminating the nuanced health effects of vaping, the broader aim is to foster actionable insights that deepen public understanding and motivate healthier, long-term choices. By nurturing a dialogue grounded in empathy, scientific rigor, and compassion, society can better support individuals looking to protect and promote their well-being. Remaining informed and actively engaged with the latest scientific research is crucial, serving as a powerful compass that can guide individuals towards safer and more health-conscious futures.