An In-Depth Look at the Conrad Peutinger II 1475
The Conrad Peutinger II 1475 map offers a unique window into the past, connecting ancient civilizations with modern historical interpretations. Far more than just a parchment covered in lines and markings, this artifact reveals stories of ancient trade routes, cultural exchanges, and significant historical events. Whether you’re a history buff or simply intrigued by how our ancestors navigated their world, the Conrad Peutinger II 1475 map is filled with mysteries waiting to be explored. Let’s delve into the rich history, importance, and the ongoing debates that surround this fascinating piece of cartography.
The Historical Roots and Origins of the Conrad Peutinger II Map

Commissioned in 1475, the Conrad Peutinger II map is a significant relic from the medieval era, reflecting the Renaissance spirit of exploration and knowledge. Humanist scholar Conrad Peutinger was behind this monumental work, aiming to compile geographical knowledge from ancient Roman sources. This map represents a fusion of historical and contemporary geographic data, highlighting the Renaissance dedication to preserving classical knowledge in a rapidly changing world.
Peutinger’s collaboration with skilled cartographers resulted in a unique document that offers modern historians invaluable insights into how people of the time perceived their world. Each feature on the map tells a story about the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations, making it a crucial resource for those studying the past.
A Detailed Exploration of the Map’s Features
The Conrad Peutinger II map is an extraordinary example of cartographic art, stretching an impressive 3.5 meters in length. This map offers a distinct portrayal of the Roman Empire’s geography, showcasing the intricate network of cities, roads, and landmarks that were essential for trade and travel.
The map’s unique linear format emphasizes routes rather than distances, a design choice that sets it apart from modern maps. The vibrant illustrations breathe life into the regions depicted, with stylized mountains and flowing rivers that add an artistic flair. Every element on the map is meticulously crafted, serving both as a practical tool for navigation and an educational resource for scholars of the time.
This blend of functionality and artistry contributes to the map’s enduring historical value, offering a glimpse into how ancient people visualized their world.
The Enduring Significance and Modern Applications of the Map
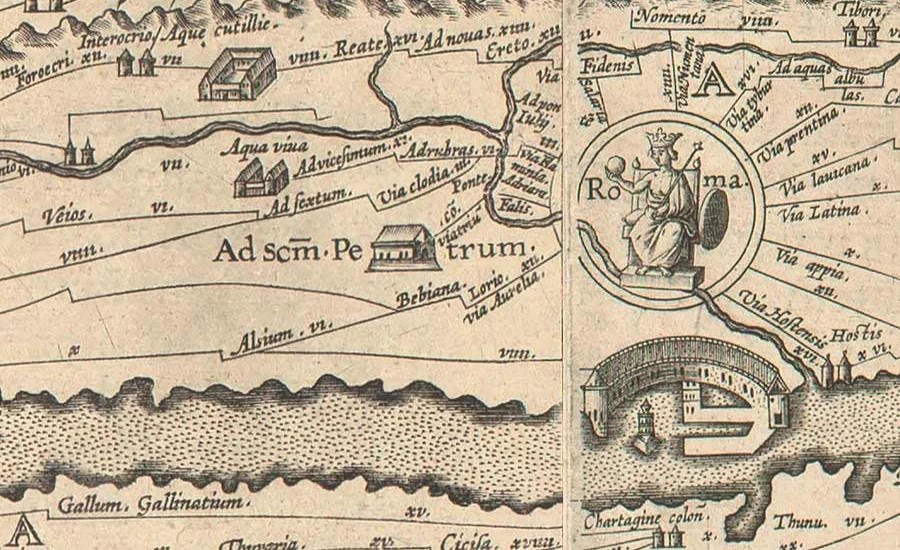
The Conrad Peutinger II map is a vital artifact for those studying historical geography, providing a detailed account of how ancient civilizations understood their world. It highlights key trade routes and cities, offering insights into the Roman Empire’s infrastructure at its height. Historians and archaeologists utilize this map to uncover valuable information about the economic systems and cultural exchanges that shaped the ancient world.
Beyond academic circles, the map has influenced modern culture. Artists and filmmakers frequently draw upon its imagery to evoke themes of exploration and adventure. Additionally, contemporary cartographers study the map’s intricate details, using them as inspiration for modern mapping techniques. The Conrad Peutinger II map continues to influence how we represent geography today, blending artistic creativity with informative precision.
Efforts in Preserving and Accessing the Map
Preserving the Conrad Peutinger II map is crucial for both historical research and public education. Given its age and fragility, careful measures are taken to protect this artifact from environmental damage. Archival institutions around the world are involved in the preservation process, ensuring that this valuable resource remains intact for future generations.
Advances in digital technology have made the map more accessible than ever before. High-resolution digital scans allow scholars and enthusiasts worldwide to study the map without risking damage to the original. Replicas and digital displays are frequently featured in exhibitions, bringing the map’s historical significance to a broader audience.
With the growing availability of online databases and academic resources, anyone interested in the Conrad Peutinger II 1475 map can easily explore its rich history and detailed craftsmanship from anywhere in the world.
Debates and Controversies Surrounding the Map
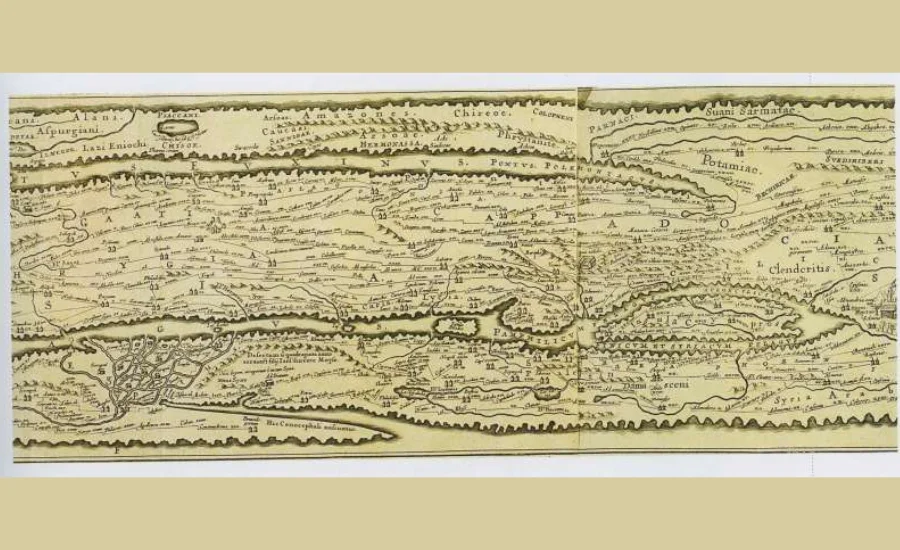

The Conrad Peutinger II map has been the subject of much debate among historians and cartographers. Some critics argue that the map, while impressive, contains notable inaccuracies that reflect the limited knowledge of the time.
Another area of controversy is the map’s Eurocentric perspective, which some scholars believe marginalizes other cultures and geographies. This debate raises important questions about the inclusivity and objectivity of historical documentation.
The interpretation of the map’s symbols has also sparked debate. While some see them as mere artistic flourishes, others argue that they obscure important information about ancient trade routes and cities. Ownership disputes over the original copies of the map further complicate its history, with various institutions claiming rights to different versions.
These controversies underscore the complexities involved in interpreting historical artifacts. As new discoveries and perspectives emerge, our understanding of the Conrad Peutinger II 1475 map continues to evolve, highlighting the dynamic nature of historical scholarship.
The Map’s Influence on Renaissance Thought and Exploration
The creation of the Conrad Peutinger II map during the Renaissance was not just a scholarly endeavor but also a reflection of the era’s broader intellectual currents. The Renaissance marked a period of renewed interest in classical antiquity, and Peutinger’s work was emblematic of the humanist desire to recover and preserve ancient knowledge.
This map, with its detailed representation of the Roman Empire, inspired a generation of explorers and thinkers who were eager to expand their understanding of the world. The depiction of vast trade routes and cities served as a catalyst for further exploration and expansion during the Age of Discovery, influencing figures such as Christopher Columbus and Vasco da Gama.
Cultural Depictions and the Artistic Legacy of the Map
Beyond its practical applications, the Conrad Peutinger II map has left a lasting impact on the arts. The map’s intricate designs and symbolic representations have been featured in numerous works of art, from Renaissance paintings to modern graphic novels.
Artists have drawn inspiration from the map’s rich imagery, often using it to convey themes of exploration, discovery, and the passage of time. The map’s visual elements—such as the stylized landscapes and roads—have been reinterpreted in various artistic mediums, making it an enduring symbol of the interplay between art and science.
Exploring the Map’s Symbolism and Hidden Meanings
While the Conrad Peutinger II map is primarily valued for its geographical information, it also contains layers of symbolism that reflect the worldview of its creators. The use of certain symbols and artistic motifs can be seen as a commentary on the political and cultural dynamics of the time.
For instance, the prominence of Roman cities on the map could be interpreted as a statement about the enduring legacy of the Roman Empire, while the omission or downplaying of non-European regions might reflect the Eurocentric perspectives of Renaissance scholars.
Scholars continue to study these symbols, uncovering new insights into the map’s deeper meanings and the historical context in which it was created.
Future Research and Technological Innovations in Map Analysis
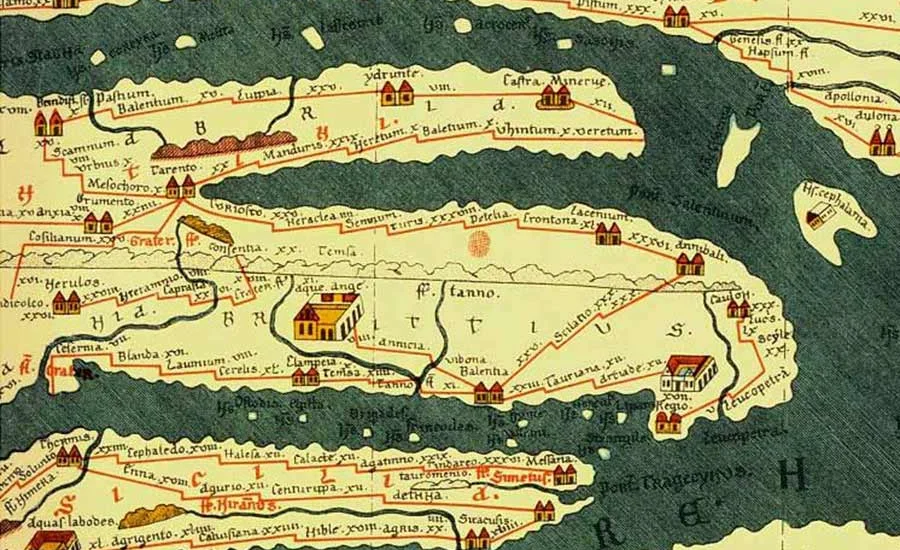
The study of the Conrad Peutinger II map is far from complete. As technology advances, new tools and methodologies are being developed to analyze historical maps with greater precision. Techniques such as digital reconstruction, 3D modeling, and geographic information systems (GIS) are opening up new possibilities for understanding the map’s content and its creation.
Future research may uncover previously unnoticed details or reinterpret existing knowledge, further enhancing our understanding of this remarkable artifact. The ongoing analysis of the Conrad Peutinger II 1475 map ensures that it will remain a subject of scholarly interest for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Conrad Peutinger II 1475
Q: What is the Conrad Peutinger II Map of 1475?
A: The Conrad Peutinger II map of 1475 is a medieval artifact that provides a detailed representation of the Roman Empire’s geography. Commissioned by Conrad Peutinger, a humanist scholar, the map combines ancient Roman geographic knowledge with contemporary data, making it a valuable resource for understanding the world as perceived during the Renaissance.
Q: What makes the Conrad Peutinger II map unique?
A: The map is unique due to its linear format, which emphasizes routes rather than distances, and its extensive depiction of the Roman Empire’s infrastructure. It also stands out for its artistic elements, such as stylized mountains and rivers, which blend functionality with aesthetic appeal.
Q: What are some of the controversies surrounding the map?
A: The map has sparked debates regarding its geographical accuracy, its Eurocentric perspective, and the interpretation of its symbols. Some scholars argue that it contains inaccuracies reflective of the time’s limited knowledge, while others question its portrayal of non-European regions.
Q: How is the Conrad Peutinger II map preserved today?
A: The map is preserved through careful archival practices, with institutions worldwide involved in its protection. Advances in digital technology have also made high-resolution scans of the map available, allowing for broader access without risking damage to the original artifact.
Q: Can I view the Conrad Peutinger II map online?
A: Yes, digital versions of the Conrad Peutinger II map are available online through various academic databases and archival institutions. These digital scans provide an accessible way for scholars and enthusiasts to study the map in detail.
Q: What role did the map play in the Renaissance?
A: The map played a significant role in the Renaissance by preserving and disseminating classical geographic knowledge. It influenced explorers and thinkers during the Age of Discovery, inspiring further exploration and contributing to the era’s broader intellectual currents.
Q: What are the future prospects for research on the Conrad Peutinger II map?
A: Future research on the Conrad Peutinger II map will likely benefit from technological innovations such as digital reconstruction, 3D modeling, and GIS. These tools will allow for more precise analysis and could lead to new discoveries about the map’s content and creation.
Conclusion
The Conrad Peutinger II 1475 is a significant historical artifact that provides valuable insights into the geographic understanding of the Roman Empire during the Renaissance. Commissioned by humanist scholar Conrad Peutinger, this map merges ancient Roman knowledge with contemporary data, showcasing its artistic and functional importance. Notable for its impressive length, linear format, and vivid illustrations, the map details ancient trade routes, cities, and landmarks, making it an essential resource for historians, archaeologists, and cartographers.
However, it is also the subject of debates regarding its geographical accuracy, Eurocentric perspective, and symbolic interpretations, adding complexity to its study. Beyond its academic influence, the map has impacted Renaissance thought and the arts, with its symbolism continuing to inspire scholarly exploration. Preserved through digital scans and exhibitions, the Conrad Peutinger II Map remains a vital artifact for understanding ancient civilizations, with future technological advancements promising even deeper insights.
Don’t miss out on updates and alerts – stay connected! Twinkle Crest