Starting your own garden can be an incredibly rewarding experience. Whether you dream of cultivating vibrant flowers, growing your own vegetables, or simply enhancing the beauty of your outdoor space, gardening offers a chance to connect with nature and enjoy fresh, homegrown produce. If you’re a beginner, the process might seem intimidating, but with a little knowledge and patience, anyone can go from seed to sprout. Here’s a guide to help you get started with your very first garden.
1. Choose the Right Location
One of the first steps in starting a successful garden is selecting the ideal location. Most plants thrive in a spot that receives at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day. Whether it’s a backyard, balcony, or windowsill, ensure your chosen area has adequate sunlight, as this is crucial for plant growth.
In addition to sunlight, consider the soil quality in your chosen spot. Ideally, you want well-drained, fertile soil. If your soil is sandy or clay-heavy, you can amend it with compost or organic matter to improve its texture and nutrient content. For those with limited outdoor space, container gardening is a great option, and it allows you to control soil conditions more easily.
2. Select the Right Plants for Your Region
Choosing the right plants for your garden is key to ensuring success. Take into account your climate zone, the amount of sunlight available, and the time of year when deciding what to plant. Some plants, like tomatoes, peppers, and herbs, prefer warmer temperatures, while others, such as lettuce, peas, and spinach, thrive in cooler weather.
You can find helpful information about which plants are best suited to your area by checking your local gardening center or looking up the USDA Hardiness Zone Map. It’s also helpful to know whether the plants you select are annuals (which need to be replanted every year) or perennials (which return year after year).
3. Prepare Your Soil
Healthy soil is the foundation of a thriving garden. Before planting your seeds or seedlings, take the time to prepare your soil properly. Start by removing any weeds or grass that might compete for nutrients and water. You can use a hoe or hand tools to clear the area, or in the case of larger plots, consider using a tiller.
Next, improve the soil by adding compost, manure, or organic matter. This will enrich the soil with essential nutrients and improve its structure, allowing for better root growth and water retention. Mixing in organic material also promotes the development of beneficial microorganisms that will support plant health.
If you’re gardening in containers, use a high-quality potting mix that’s designed for the type of plants you’re growing. Avoid using regular garden soil in containers, as it can compact over time and hinder root development.
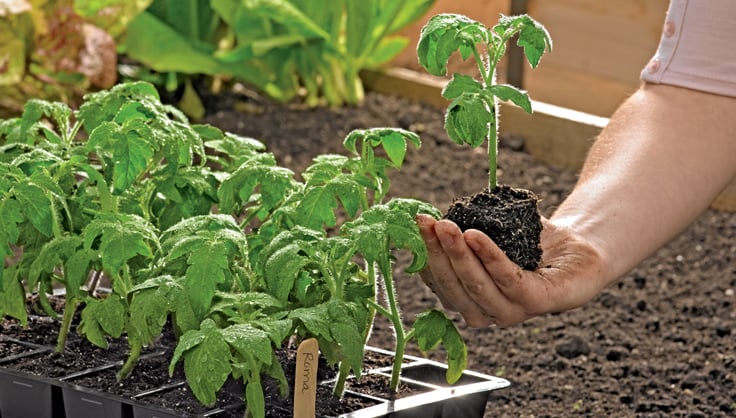
4. Planting Your Seeds or Seedlings
Once your soil is prepared, it’s time to start planting. If you’re using bulk vegetable seeds, make sure to follow the instructions on the seed packet for proper planting depth and recommended spacing. Some seeds need only a light covering of soil, while others should be planted deeper.
Keep in mind that bulk vegetable seeds often require more careful spacing, as planting too closely can lead to overcrowding, which can stunt growth and reduce airflow.
For seedlings, dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball, ensuring the plant will be level with the surrounding soil. Gently remove the seedling from its container, loosen the roots if they’re tightly packed, and place it in the hole. Fill the hole with soil and water gently to help the plant settle. Always account for the spacing needs of each plant, as this will promote healthy growth and reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
5. Watering Your Garden
Watering is crucial to a garden’s success, but it’s important not to overwater. The general rule of thumb is to water deeply and infrequently, rather than lightly and often. This encourages roots to grow deeper into the soil and makes the plants more drought-resistant in the long run.
The best time to water is early in the morning, before the heat of the day, or in the evening when the sun’s intensity has lessened. Avoid watering during the hottest part of the day, as this can lead to evaporation and plant stress.
When watering, focus on the roots and try to avoid wetting the foliage, as wet leaves can promote fungal diseases.
6. Mulching for Moisture Retention
Mulch is a garden’s best friend when it comes to retaining moisture, suppressing weeds, and keeping the soil temperature consistent. Apply a 2-3 inch layer of organic mulch, such as straw, wood chips, or shredded leaves, around your plants. Not only will this help reduce the need for frequent watering, but it will also protect the soil from extreme temperature fluctuations and prevent erosion.
7. Fertilizing for Growth
While soil amendments like compost can provide essential nutrients, your plants may also benefit from additional fertilization during the growing season. Look for a balanced fertilizer with equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (N-P-K) to encourage healthy growth.
Always follow the instructions on the fertilizer package to avoid overfeeding, which can harm plants and the environment. Organic fertilizers, such as fish emulsion or compost tea, are gentle and less likely to damage your garden, especially for beginners.
8. Monitor and Care for Your Plants
As your garden grows, it’s important to monitor for signs of pests and diseases. Regularly inspect your plants for insects, discolored leaves, or signs of wilting. If you notice any issues, act quickly to prevent further damage. Many common pests, such as aphids or slugs, can be controlled with natural methods like introducing beneficial insects or using organic insecticidal soap.
Pruning your plants when necessary will also promote healthy growth. Remove dead or yellowing leaves to help direct energy to healthy parts of the plant, and trim back any excessive growth to encourage air circulation.
9. Enjoy Your Harvest
The best part of gardening is harvesting the fruits (and vegetables) of your labor. Depending on what you’ve planted, some crops may take several months to mature, while others can be harvested in just a few weeks. Be sure to pick your produce at its peak, as this is when the flavor and texture are the best.
Gardening can be a learning experience, so don’t be discouraged by small setbacks. With patience, practice, and the right care, your garden will flourish, bringing beauty and bounty into your life. So, roll up your sleeves, get your hands dirty, and enjoy the wonderful journey from seed to sprout!